What is Deep Learning?
Definition
A fantastic quote by Arthur Samuel, summarises Deep Learning (DL) as:
“Some automatic means of testing the effectiveness of any current weight assignment in terms of actual performance and provide a mechanism for altering the weight assignment so as to maximize the performance”
by Arthur Samuel in Fastai Book, Chapter 1
Core Processes of Deep Learning:
Decomposing the above statement, we can better understand the three core processes that underpin DL operation:
| Term | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Weight Assignment | Parameters (weights) that process inputs to yield output(s) |
| Mechanism | Automatically adjust the weight assignments to optimise performance. |
| Actual Performance | The overall quality of the output. That is, the degree by which the test loss. |
DL Functionality
To develop a mechanism that can measure performance of a model, the DL architecture must be capable of:
- Comparing a winning and losing model
- From this, determine a winning direction
- So it can, learn from each iteration, improving with experience
Thus, the DL model can be visually described as shown below:
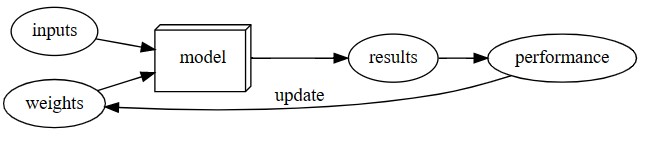
Image Source: Fastai Book, Chapter 1
Reference List
https://nbviewer.org/github/fastai/fastbook/blob/master/01_intro.ipynb